As with any e-commerce site, it is important for users to know the terms and conditions and privacy policy that your site offers. This is for their own safety and yours as well.
This section allows you to set up your pages for your privacy policy, return policy, terms of use and shipping policy to be presented to customers.
Fields
The model used is Shopper\Core\Models\Legal.
| Name | Type | Required | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
id |
autoinc | auto | |
title |
string | yes | Unique, title of the legal page |
slug |
string | yes | Unique, this is dynamically generated based on the title |
content |
longText | no | nullable, the text of the legal page |
is_enabled |
boolean | no | Default false, define if this legal page is ready to use |
Components
The components used to manage Legal page are found in the component configuration file config/shopper/components.php. Each component corresponds to the page that is defined
use Shopper\Http\Livewire\Components; return [ ... 'livewire' => [ ... 'settings.legal.privacy' => Components\Settings\Legal\Privacy::class, 'settings.legal.refund' => Components\Settings\Legal\Refund::class, 'settings.legal.shipping' => Components\Settings\Legal\Shipping::class, 'settings.legal.terms' => Components\Settings\Legal\Terms::class, ... ]; ...];Add Legal content
In your administration area you must click on the "cog" icon to display the settings page of your store.
- From your admin panel, on the blue sidebar click on the cog icon, go to
Settings > Legal.
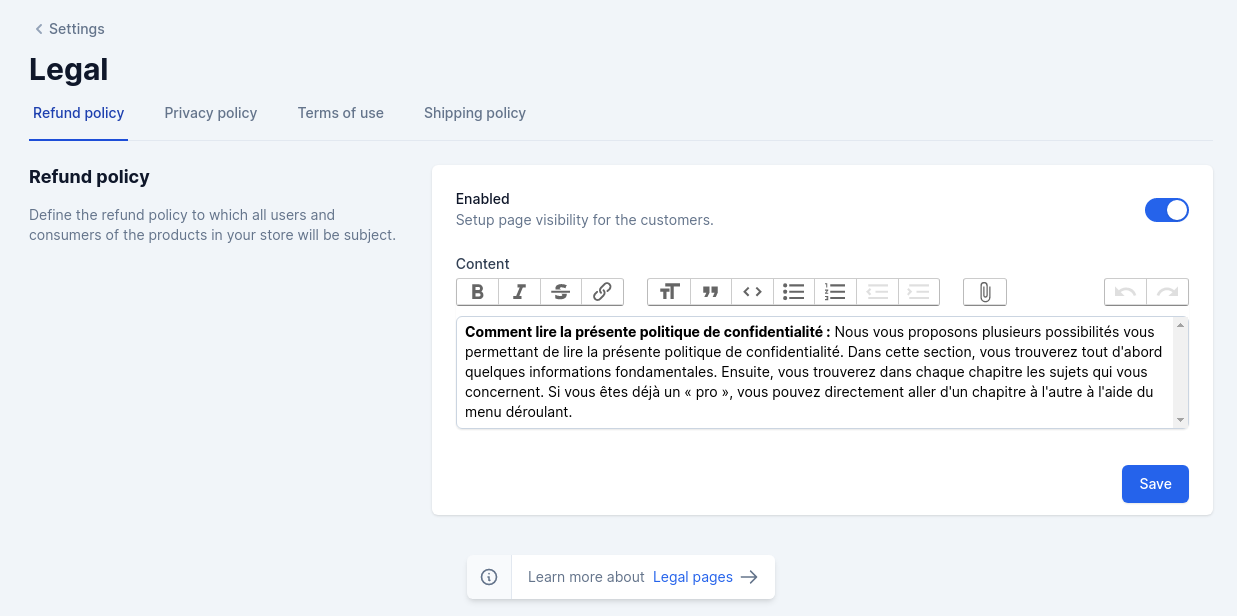
Once in this page, all the legal pages are displayed as a tab. You can just fill in the content of each page and click on the Enable switch to retrieve the content of your page and display it in your front-end.
Retrieve Data
Once the information is filled in, we can display it to our users in the views we have created.
To do this we will start by creating a controller that will take care of collecting our information and send it to a view
php artisan make:controller LegalControllerWe will add the functions for each of our pages and return the information to present them to our users. Our controller will look like this
namespace App\Http\Controllers; use Shopper\Core\Models\Legal; class LegalController extends Controller{ public function privacy() { return view('legal.privacy', [ 'legal' => Legal::enabled()->where('slug', 'privacy-policy')->first(), ]); } public function refund() { return view('legal.refund', [ 'legal' => Legal::enabled()->where('slug', 'refund-policy')->first(), ]); } public function terms() { return view('legal.terms', [ 'legal' => Legal::enabled()->where('slug', 'terms-of-use')->first(), ]); } public function shipping() { return view('legal.shipping', [ 'legal' => Legal::enabled()->where('slug', 'shipping-policy')->first(), ]); }}Legal::enabled() is a scope to retrieve the page only when it is available. This is a simple way to retrieve the pages but you can do it otherwise all the front-end code depends on you. To learn more about the scopes you can consult the documentation.
Routes
Once we have created the controllers we will associate the routes that will allow us to display our contents. We will display our content in the web.php.
use App\Http\Controllers\LegalController; /** Legal routes*/Route::get('/privacy', [LegalController::class, 'privacy'])->name('legal.privacy');Route::get('/terms-of-use', [LegalController::class, 'terms'])->name('legal.terms');Route::get('/refund-policy', [LegalController::class, 'refund'])->name('legal.refund');Route::get('/shipping', [LegalController::class, 'shipping'])->name('legal.shipping');Views
You can create views in this way to arrange the content of your legal pages.
resources/views/legal/ privacy.blade.php terms.blade.php refund.blade.php shipping.blade.phpExample of a view
@extends('layouts.app') @section('body') <x-legal-layout> <x-slot name="title"> <h2 class="text-2xl font-bold uppercase text-dark tracking-wider font-heading sm:text-3xl"> {{ __('Privacy Policy') }} </h2> <span class="text-sm leading-5 text-gray-500">{{ __('Last update: :date', ['date' => $legal->created_at->format('d, F Y')]) }}</span> </x-slot> {!! $legal->content !!} </x-legal-layout> @endsection